The history of BOTOX®
BOTOX® (onabotulinumtoxinA) is a type of medicine that is used to treat patients with certain neuromuscular conditions. One of the most researched medicines in the world, BOTOX® treatment is approved for medical uses across the world.

Since its FDA approval for aesthetic treatment in April 2002, the neurotoxin Botox has gone from a somewhat controversial treatment to a celebrity-endorsed wrinkle remedy. Injectables have become the new norm in cosmetic treatment. According to the American Academy of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, the most common nonsurgical procedures last year were Botox and hyaluronic acid fillers.
It’s come a long way from its origins as an FDA approved treatment for two rare eye muscle disorders (strabismus and blepharospasm). The original name, Oculinum, doesn’t exactly roll off the tongue, but shortly after Allergan secured that first FDA approval in 1989, the product was rebranded Botox. Once physicians realized that Botox could treat wrinkles, the rest was history.
Botox reached nearly $1.6 billion in sales last year, attributing 51 percent to therapeutic uses and 49 percent to aesthetic uses. It became so successful that it gained its first FDA-approved wrinkle-reducing competitor in 2009-the sincerest form of flattery in the business world. However, Botox continues to evolve as new uses for the product are discovered. Used off-label, it treats a host of concerns such as crow’s-feet, down-turned corners of the mouth and bands on the neck. You may be surprised to learn that it has also been used, off label, to aesthetically treat enlarged pores, droopy eyebrows, a pointy chin and a droopy nose tip. Additionally, it’s an FDA-approved treatment for medical conditions ranging from chronic migraine to excessive sweating. Next up: the company is seeking FDA approval for the treatment of crow’s-feet.
1950s- Scientists discover that botulinum toxin can reduce muscle spasms.
1960s/1970s- Studies explore botulinum toxin as a treatment for strabismus (crossed eyes).
1988- Allergan researches other medical uses of botulinum toxin.
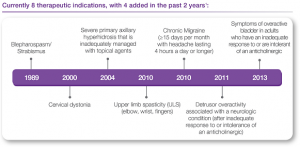
1989- Allergan introduces BOTOX®, the first botulinum toxin approved by the FDA to treat blepharospasm (eyelid spasms) and strabismus.
2000- FDA approves BOTOX® therapy for cervical dystonia to reduce the severity of abnormal head position and neck pain.
2002- FDA approves BOTOX® Cosmetic (onabotulinumtoxinA), the same formulation as BOTOX®, with dosing specific to moderate to severe frown lines between the brow.
2004- FDA approves BOTOX® for severe underarm sweating when topical medicines don’t work well enough.
2009- 20-year anniversary of BOTOX®
2010- FDA approves BOTOX® therapy for increased muscle stiffness in elbow, wrist, and finger muscles with upper limb spasticity.
Compared to other cosmetic procedures, BOTOX® offers patients many benefits with its convenience, effectiveness and affordability. The entire procedure takes about ten minutes to perform, and patients can go home and return to regular activities immediately after. The results of BOTOX® injections are visible within the next few days.
At Dr. Bishara’s office we have weekly Botox specials in our Mansfield and Southlake office locations. Please call our office at (817) 473-2120 to find out more about our weekly Botox specials or visit our website at www.MarkBisharaMD.com.





